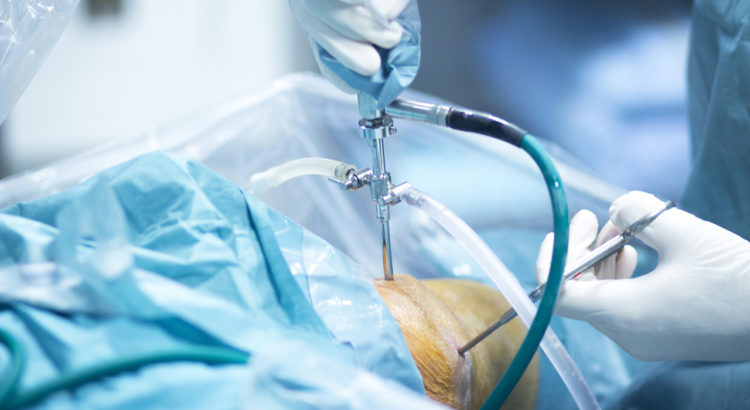
External Fixation
An external fixator acts as a stabilizing frame to hold the broken bones in proper position. In an external fixator, metal pins or screws are placed into the bone through small inc
251 Beded well equipped Multispecialty Hospital
 0141-278 0760
0141-278 0760Call Us Now - 24/7 Customer Support
Dr. Rajendra Prasad Saini , MBBS, MS (Chief Orthopedic Surgeon)
Dr. Ojas Saini MS Ortho DNB (Bone & Joint Specialist), KEM Mumbai
Dr. Anil Marotiya (Sr. Resident)
Dr. Alokeshwar (Resident)
Dr. Aman Saah (Resident)
Orthopedic - 24*7 and 365 days open X Ray and Fracture Clinic.
The Pediatric Orthopedic service @ Dhanwantari Hospital provides state-of-the art treatment for infants, children and adolescents with orthopedic and bone & joint related conditions. Dhanwantari Hospital has pediatric orthopaedic surgeons, pediatric radiologists, and pediatric anaesthesiologists who specialize exclusively in the care of children. This creates an environment that is comfortable and safe for your child. . It is our mission to provide a diagnosis and treatment in a timely fashion and in the best environment to your child.
Our team of pediatric orthopaedic surgeon, physiotherapist is specialty fellowship trained to treat a wide range of conditions affecting children’s bones, joints, and muscles. We provide non-surgical and surgical care variety of conditions.
Some of the conditions that we treat include:
Conditions treated for Ped Ortho
Perthes disease : - Perthes disease is a disease of the hip in which the bone in the hip joint loses its blood supply. This may cause the bone (femur) to change shape so that it no longer fits into the hip joint (femoral head) properly. The disease run a 2-year course, and if left untreated, can cause permanent damage to the bone.
Myotonic dystrophy - Myotonic dystrophy, also known as Steinerts’s disease, is the most frequently diagnosed adult form of muscular dystrophy. It is characterized primarily by progressive muscle weakness and muscle wasting and by myotonia (difficulty in relaxing a muscle or a group of muscles following contraction). It is a multisystem disease, typically involving a wide range of other tissues as well as muscle.
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) - Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a genetic disorder of type 1 collagen—the protein “scaffolding” of bone and other connective tissues. People with OI have a faulty gene that instructs their bodies to make either too little type 1 collagen or poor quality type 1 collagen. The result is bone that break easily. Four forms of osteogenesis imperfecta have been described, representing wide variation in appearance and severity. Below are the clinical features of the four major types of OI. Clinical features vary widely not only between types, but within types, and even within the same family.
Simple Bone Cyst (SBC) : - Bone Cyst is a curable condition. Spontaneous resolution after a fracture is known. Success rate with Intra-Lesional Steriod and Bone Marrow is about 80%. Currettage, bone grafting and intra-lesional rodding with titanium implants or screws have over 90 % success rate in curing the lesion.
Surgery in Cerebral Palsy - Management of children with cerebral palsy need an integrated approach. A systematic assessment is carried out prior to surgery to identify the goals of SEMLS or PERCS for that particular child and to determine what is called the “Surgical Dose” required to achieve optimum results. The surgery is planned after thorough discussion with the parents /caregivers and the treating physiotherapists so that the post-operative rehabilitation protocol is tailored to the individual child. Appropriate orthotics are also fabricated so that plaster immobilization is minimal to prevent muscle disuse.
Congenital Dislocation of the Hip ,(CDH) - The most common cause of CDH is looseness (laxity) of the ligaments surrounding the hip. This is likely due to fetal absorption of the maternal hormones that increase pelvic relaxation just before delivery uterine compression, which forces the infant’s hips into a flexed position and limits fetal movement, is also thought to play a role in CDH. Sometimes the way the newborn child is held or is placed in the crib may contribute to the development of hip instability and subsequent dislocation.
Scoliosis - Scoliosis is a lateral [sideways] curvature of the spine that usually develops in preadolescence or during early adolescence. In most cases the curve is slight, but in severe cases, it can resemble either an S or C in shape. The normal spine appears curved when viewed from behind. In scoliosis, the opposite is true; the spine appears straight when viewed from the side yet curved from behind.
Torticollis - This is a common soft tissue problem in neonates and may co-exist with developmental dysplasia of the hip joint (DDH) and calcaneovalgus foot. Over 90% may resolve spontaneously by six to 12 months. 10 % cases need physiotherapy and about 5 % of these may progress to a rigid deformity.Once the deformity is established, surgery is usually recommended by four years of age to prevent or reverse the secondary associated features such as facial hypoplasia and improve the visual field.
Slipped Capital Femroal Epiphysis (SCFE) - SCFE is a common hip pathology seen more frequently in boys than girls during the adolescent growth spurt. There is a mechanical weakening between the met- aphyses of the femoral neck and head causing the epiphysis to slip posteriorly.

Senior Consultant Orthopedics Surgeon DIRECTOR, DHRC JAIPUR

Orthopeadic Surgeon

Bone & Joint Specialist, Managing Director
An external fixator acts as a stabilizing frame to hold the broken bones in proper position. In an external fixator, metal pins or screws are placed into the bone through small inc